Why is private health insurance in Germany superior?
Depending on your professional and financial situation, you can choose between private or statutory health insurance in Germany. Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, which we should talk about.

Time as Currency: How Public Insured Patients 'Pay' with Their Wait for Healthcare


Differences between Private Health Insurance (PKV) and Statutory Health Insurance (GKV)
Outpatient treatment

GKV: Treatment options are limited to contracted physicians of the GKV. They provide essential medical care, focusing on treatments aimed at restoring health based on economic considerations.

PKV: Select the healthcare provider of your choice, whether it be a primary care physician or a specialist, without the hassle of a referral. Enjoy reduced wait times for appointments and the freedom to explore alternative treatment options that cater to your individual needs and preferences.
Dental treatment

GKV: This plan covers essential dental treatments, providing you with peace of mind knowing that your basic oral health needs are taken care of. However, when it comes to premium dental restorations, you may find yourself reaching deep into your pockets to ensure you receive the highest quality care for your smile.

PKV: PKV offers a wide range of services dedicated to dental prosthetics and treatments, ensuring that patients receive top-notch care and high-quality dental replacements. With the added benefit of full reimbursement for these services, our patients can rest assured that their oral health needs are being met with the utmost excellence and affordability.

What extra costs can I expect at the dentist?
| Treatment | Root Canal | Inlay | Implant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invoice Amount | €1,600 | €600 | €3,300 |
| GKV (Statutory Health Insurance) Pays | €350 | €40 | €420 |
| Out-of-Pocket without Dental Supplement | €1,250 | €560 | €2,880 |
| Out-of-Pocket with Dental Supplement | €1,250 | €560 | €2,880 |
This table provides an overview of the expected co-payments for different dental treatments, considering reimbursements by statutory health insurance (GKV) and the patient's share of the cost, both with and without additional dental supplementary insurance. The calculation example takes into account the tariff reimbursement based on the invoice amount.

Inpatient Care

GKV: Enjoy the comfort of shared room accommodation while receiving personalized treatment by our experienced team of ward doctors. Rest assured that you will receive top-notch care in a cozy and welcoming environment.

PKV: Experience personalized care with our PKV plan, where you can enjoy the comfort of a private room and have the freedom to choose your preferred hospital. Benefit from top-notch treatment delivered by our experienced head physician, ensuring the highest quality of care tailored to your individual needs.
Who do you entrust your health to?
|
|
 |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Resident Doctor | Specialist Doctor | Senior Physician | Head Physician |
| Little experience (recent graduate) | At least 5 years of experience | Highly experienced | Extensive and specialized experience |
| Practical training | Independent patient treatment | Responsible for medical treatment in the department, supports specialists | Overall responsibility for medical treatments and department management |
| Supervised by experienced doctors | Works independently | Supervises residents, point of contact for specialists | Oversees all doctors and processes in the department |
Please select the treatment you desire.
| Treatment Option | Standard Care | Standard Maximum Rate | Above Fee Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invoice Amount | €32,000 | €74,670 | €117,330 |
| GKV (Statutory Health Insurance) Pays | €32,000 | €32,000 | €32,000 |
| Out-of-Pocket without Supplementary Insurance | €0 | €42,670 | €85,330 |
| Out-of-Pocket with Supplementary Insurance | €0 | €42,670 | €85,330 |
This table comprehensively compares various treatment options within the German health insurance system.
Highlighting invoice amounts, statutory health insurance coverage, and out-of-pocket costs for patients with and without supplementary insurance.
Invoice amounts are based on average values from the GOÄ, and "Above Fee Schedule" calculations are at 5.5 times the rate.
| Treatment Option | Standard Care | Standard Maximum Rate | Above Fee Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invoice Amount | €6,700 | €15,630 | €24,565 |
| GKV (Statutory Health Insurance) Pays | €6,700 | €6,700 | €6,700 |
| Out-of-Pocket without Supplementary Insurance | €0 | €8,930 | €17,865 |
| Out-of-Pocket with Supplementary Insurance | €0 | €8,930 | €17,865 |
This table comprehensively compares various treatment options within the German health insurance system.
Highlighting invoice amounts, statutory health insurance coverage, and out-of-pocket costs for patients with and without supplementary insurance.
Invoice amounts are based on average values from the GOÄ, and "Above Fee Schedule" calculations are at 5.5 times the rate.
| Treatment Option | Standard Care | Standard Maximum Rate | Above Fee Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invoice Amount | €32,000 | €74,670 | €117,330 |
| GKV (Statutory Health Insurance) Pays | €32,000 | €32,000 | €32,000 |
| Out-of-Pocket without Supplementary Insurance | €0 | €42,670 | €85,330 |
| Out-of-Pocket with Supplementary Insurance | €0 | €42,670 | €85,330 |
This table comprehensively compares various treatment options within the German health insurance system.
Highlighting invoice amounts, statutory health insurance coverage, and out-of-pocket costs for patients with and without supplementary insurance.
Invoice amounts are based on average values from the GOÄ, and "Above Fee Schedule" calculations are at 5.5 times the rate.
Would you be ready to explore your health insurance options?
Click below to book a free consultation with our experts. Discover the perfect coverage for you today!
_2.webp)
_2.webp)
_2.webp)
_2.webp)
_2.webp)

_2.webp)

_2.webp)


The finances of GKV and PKV have become a major concern in recent years.
As healthcare costs continue to rise, both systems face their unique challenges.
The GKV, or statutory health insurance, is funded by contributions from employees, employers, and the government.
However, rising medical costs and an aging population have strained its financial stability, leading to debates about its sustainability and the need for reforms.
%20and%20Private%20Health%20Insurance%20(PHI).webp?width=900&height=600&name=Contribution%20development%20of%20the%20Statutory%20Health%20Insurance%20(SHI)%20and%20Private%20Health%20Insurance%20(PHI).webp)
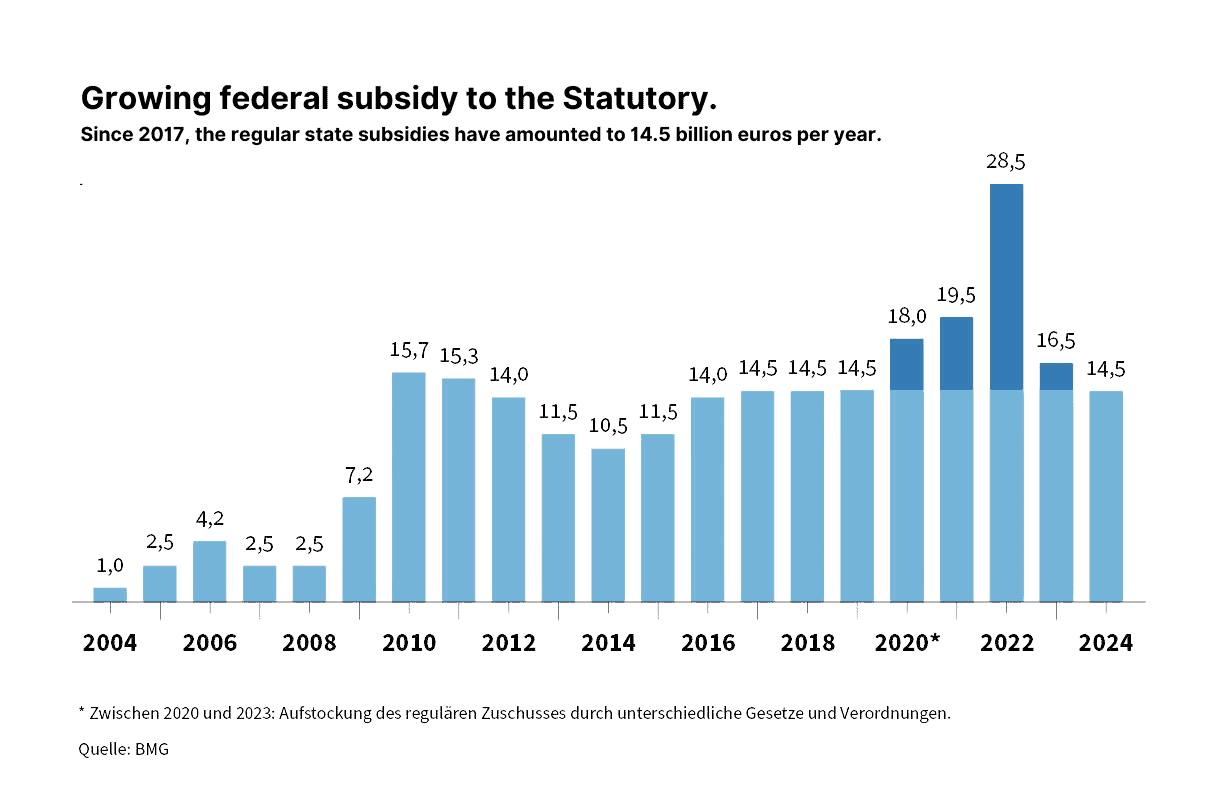
However, it is generally more expensive due to higher administrative costs and risk assessments.
Increasing healthcare costs have led private insurers to adjust their premiums, raising concerns about affordability and accessibility for those with private insurance.
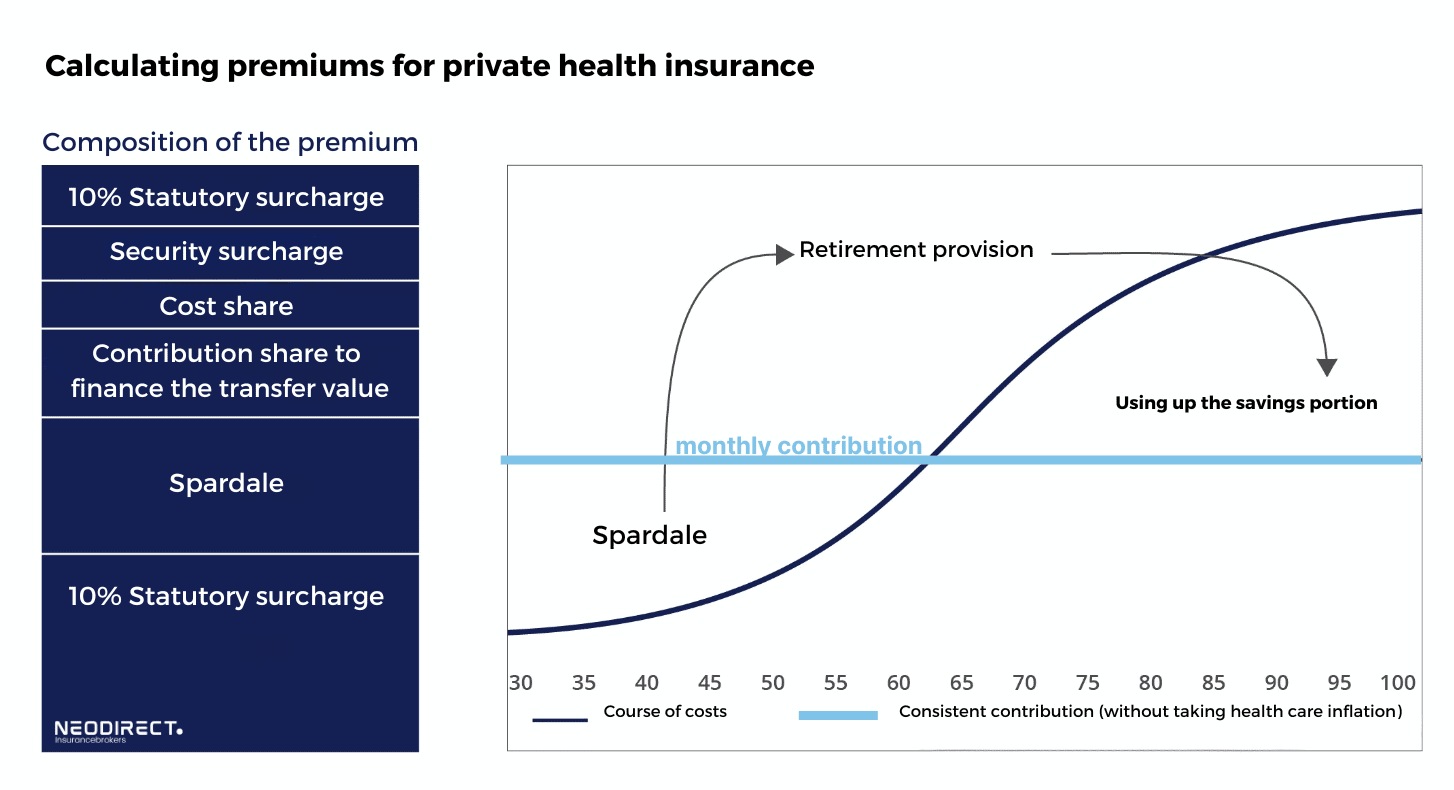
The premium calculation in private health insurance (PKV) is fundamentally different from the statutory health insurance system (GKV) and is based on several key principles:
-
Risk Principle: Unlike the GKV, where contributions are based on income, PKV premiums are calculated based on the individual risk of the insured. This includes factors such as age at entry, health status, and chosen scope of coverage.
-
Entry Age: A crucial factor in determining the premium is the age at which the insured enters the PKV. Generally, the younger the individual at entry, the lower the premium, as the risk of illness is considered lower and the insurer can accumulate more savings over time to cover future costs.
-
Health Status at Entry: Health status is assessed at the time of application through medical questionnaires or examinations. Pre-existing conditions may lead to higher premiums or exclusions of certain benefits.
-
Scope of Benefits: The level of coverage selected significantly influences the premium. Comprehensive plans with lower deductibles, broader benefits, and options such as worldwide coverage will result in higher premiums.
-
Savings Component (Aging Reserves): PKV premiums include a savings component to stabilize premiums in older age. This component builds up aging reserves that help offset the increasing health costs associated with aging, theoretically leading to more stable premiums over the policyholder's lifetime.
-
Adjustments: Premiums can be adjusted over time due to changes in medical costs, the insurer's cost structure, or legislative changes affecting insurance. These adjustments are not based on the insured's current income or health status but are applied across a certain age group or insurance pool.
-
Individual Contribution: Each insured person has an individually calculated premium. There is no family coverage where dependents are insured without additional premiums, unlike in the GKV.
-
Tax Considerations: Part of the PKV premiums can be tax-deductible, offering potential tax advantages depending on the policyholder's tax situation.
In summary, PKV premiums are tailored to the individual risk profile and coverage preferences of the insured, to provide a sustainable model that covers the insured's health costs throughout their lifetime, including building reserves for increased costs in older age.
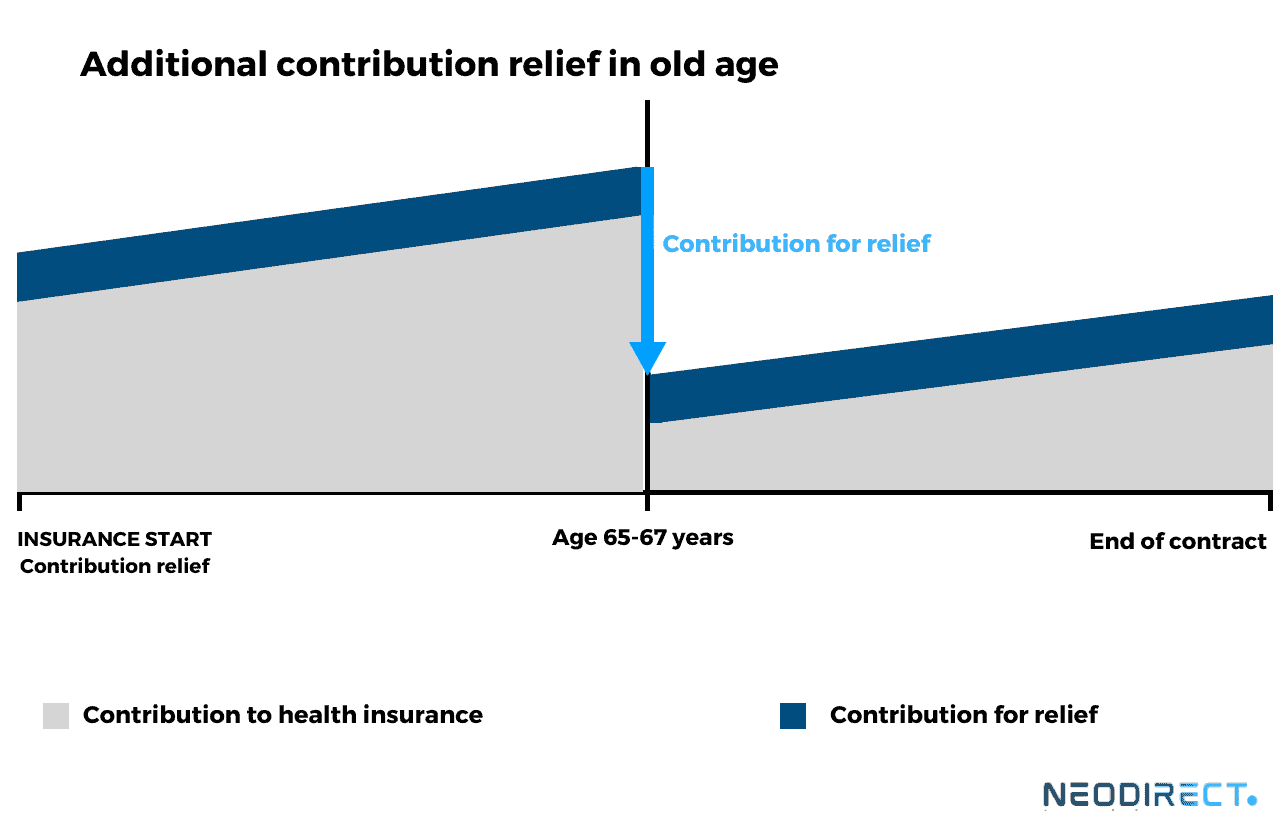
Meaningful for employees within the existing private health insurance (PHI)
Now, the contribution relief tariff comes into play. The insured can freely choose the amount of contribution, for example, from the PHI premium up to double the employer's contribution share. If the contribution relief tariff, along with the PHI premiums, stays within this range, then the contribution relief tariff is subsidized by 50% by the employer. Thus, the employee's return is a real 50%. Moreover, the contributions to the contribution relief for old age can be deducted from taxes.